|
Videnrepræsentationer i byggeprocessen
Knowledge representations in the building process
IT i Civilingeniørspeciale i Byggeledelse/IT in Building Management. 2007
1. Background
[goto top]
Udviklingen indenfor ICT de seneste årtier har indebåret øget pres på at civilingeniørers må tilegne sig ny viden for at kunne deltage aktivt i specifikation, design, implementering og evaluering af digitale informationscontainere som bruges til lagring af byggeprodukt- og byggeprocesmodeller. Det igangværende paradigmeskift fra papirbundet til digital kommunikation har vidtgående konsekvenser for vores positionering og overlevelse i det globale samfund og kræver både dyb og bred kunnen indenfor flere basale og delvis nye videndomæner.
Since the introduction of the world wide web (WWW) and standardisation of Internet services and communication protocols we can see a huge shift in the way we communicate, collaborate and handle digital knowledge. The semester 7 course focuses on models and representations of building products and processes. (In the semester 8 course we take an end user perspective on how ICT tools can support collaboration, communication and access to Internet based computer resources.)
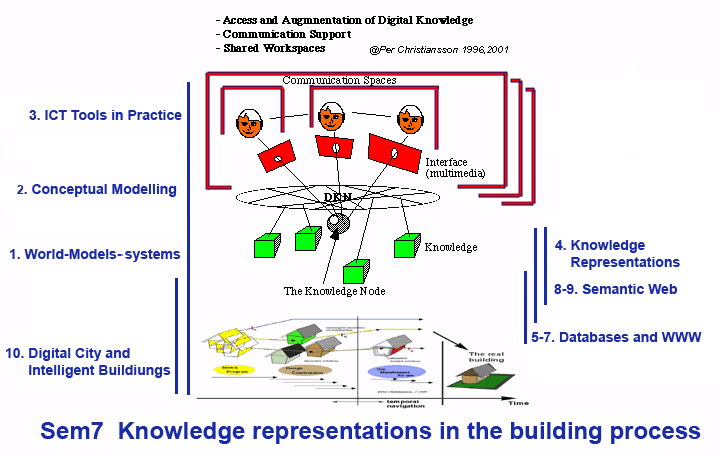
The anticipated ICT tools are only partly developed and must be designed tested and implemented in close collaboration with the building process end users. This requires that civil engineers get a deeper understanding of some knowledge domains that up till now only has been partly covered in the civil engineering curricula.
The ICT will strongly influence how we take advantage of and interact with the computer resources
- information storage and interaction media will be more separated (paper is both)
- it will be easier to adapt information containers to user needs and usage context (meta data, models interoperability, model access, etc.)
- buildings and building processes will be more effectively and efficiently represented in digital models with different knowledge representations.
- the web will form the infrastructure for information container access, and application communication
- human collaboration, team work and communication modes will be developed and partly changed
- collaboration work spaces will get a added virtual dimension being less dependent of the physical room.
The mutual influence between practice and ICT progress is necessary to maintain. Civil engineers must posses both general and some specialised ICT related knowledge to be able to specify and participate in the development of new ICT tools and to be pro-active in the process of changing work routines and company and project organisation.
This course aims at providing general knowledge on how
present and future digital product and process models can be designed and implemented as well as deeper knowledge in certain key areas such as conceptual modelling methods, different knowledge representation propereties, web-database integration, the semantic web, and model integration.
See also Building Inofrmatics Overview
and Steinman, 2004, The Job Profile of Construction Informatics
2. Goal
[goto top]
Den studerende skal opnå viden om grundlæggende koncepter, teknologier og metoder til at analysere og udvikle modeller som beskriver en bygnings funktionelle systemer, processer i byggeriet samt modeller for videnhåndtering på World Wide Web.
Den studerende skal ved den afsluttende prøve kunne:
- Beskrive hvordan processer og produkter i den virkelige verden kan beskrives som modeller der kan implementeres i IKT-støttede systemer
- Kende til hvornår forskellige konceptuelle modelleringsmetoder kan bruges
- Kende principperne og metoder for etablering af web-database kobling.
- Kende forskellige videnrepræsentationers egenskaber og disses egnethed til modellering af forskellige systemer med specielt fokus på relationsdatabaser, hypertekst og regelbaserede repræsentationer.
- Kendskab til Service Oriented Architectures til understøttelse af systeminteroperabilitet og adgang til brugerservices
- Kende principper for og opbygning af Semantic Web baserede repræsentationer inklusive kendskab til Extensible Stylesheet Language Family, XSL.
- Kendskab til opbygning af services i intelligente bygninger
3. Volume/Placement
[goto top]
This 2 modules course is one of 2 with emphasis on IT during the semester 7 Master of IT in Building Management education
(calendar).
4. Content
[goto top]
- Konceptuel modellering i IDEF0, E-R og UML
- Service Oriented Business Architecture og Service Oriented Technology Architecture
- Strukturering og modellering af relationsdatabaser.
- Structured Query Language, SQL, for relationsdatabaser
- Serverside scripting for web adgang til relationsdatabser
- Regelbaserede systemer. Introduktion til Prolog og Induktions systemer for regelgenerering.
- Hypertekstbaseret repræsentation og modellering af informationscontainere i Semantic Web
- Validering af XML-filer med brug af XML-skemaer?
- Validerring af RDF filer med brug af RDF-skemaer?
- Indlejrede systemer (embedded systems) i bygninger
5. Learning Material
[goto top]
The course content is delivered through the lectures, reading of literatur , and exercises/miniproject. It is impossible to find a set of literature that covers the course content completely. The lectures are supported by lecture slides available on the course web site. The slides with emphasized titles in the navigation bar has the same status as course literature (though not eventual references on the slide).
References to further reading is found in the lecture notes.
The coarse literature consists of both Lecture Slides and literature according to the list below.
The 'IT in Civil Engineering' site (http://it.civil.auc.dk/) also gives access to
previous years courses and if applicable mini projects. You reach it from the top of this page.
5.1 Lectures
[goto top]
The lectures are accessed from the lecture scheme below.
Each lecture has a easy to navigate slide bar and an opening slide with
short content description, questions for self assessment, references to the literature according to the literure list below and proposals for further reading.
The four hour lecture/exercise followes the scheme
- 2 hour lecture
- 1.5 hour exercise in group
- 0.5 hours exercise results presentation and follow discussions
5.2 Exercises/Mini-project
[goto top]
The exercies are also accessed from the lecture scheme below. Student group exercises results are continously updated
The exercices may well take use cases from the ongoing semester project or even be contained in a mini-project defined by the group.
The following domains will be covered during the exercices
- Write scenario(s) of the future ICT supported building process
- Conceptual modelling of your semester 7 project
- Database design and web access
- Knowledge representations
- Meta structuring of information using XML and RDF
- New services in digital cities and intelligent buildings
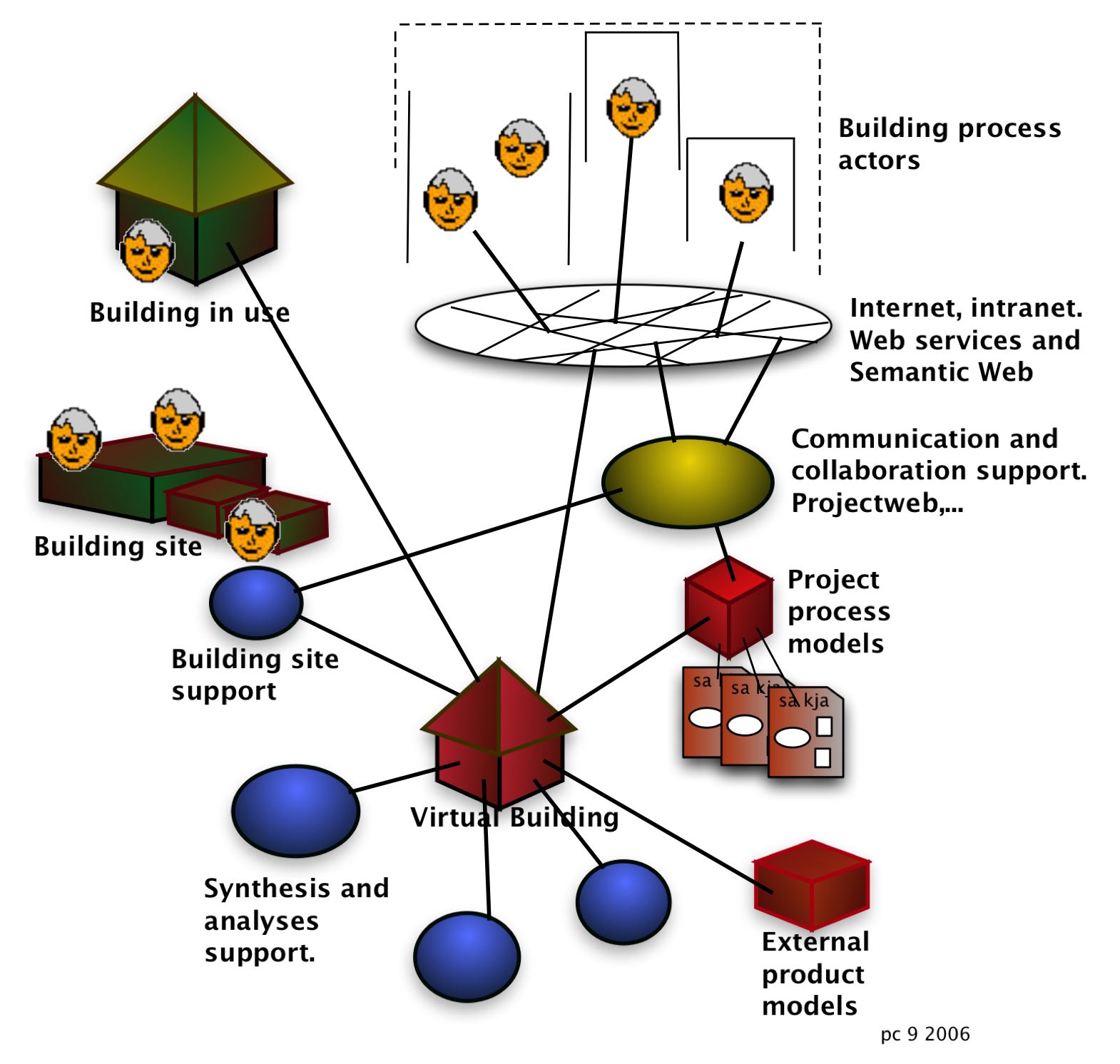
The course exercises uses modelling domains of this figure.
5.3 Software
[goto top]
The following ICT, Information and Communication tools, are available during exercises/minproject activity. (those marked with * only at the Media Lab at institute 6)
5.4 Literature
[goto top]
|
/1/
|
Christiansson P, Carlsen M (2005) Virtual Building from Theory to Practice.
Proceedings W78 22nd Conference on Information Technology in Construction. Edited by R.J. Scherer,
P. Katranuschkov, S.-E. Schapke. Dresden July 19-21, 2005. (pp. 171- 175).
|
|
/2/
|
Rasmussen Annelise, 1996, "Introduktion til IDEF0 Version 1.1". Institut for Anvendt Konstruktion og Produktion. Danmarks Tekniske Universitet. Lyngby (30 pages)
|
|
/3/
|
Miller R, 2003, "Practical UML: A Hands-On Introduction for Developers". Borland Developer Network. (7 pages).http://bdn.borland.com/article/0,1410,31863,00.html. [local].
|
|
/4/
|
Frederiksen Helle, 2000, "Databasedesign med Access 2000". IDG Forlag, Valby. (103 pp.). http://www.idgforlag.dk/. ('Centrale databasebegreber sid. 6-11, 'Normalisering'
sid. 60-63). ('Analyse' sid. 36-38, 'Dataanalyse'
sid. 51-56). ('SQL-forespørgsler'' sid. 24-28).
education/reports/access2000.pdf
|
|
/5/
|
Christiansson P, Herrera A, 1987, "Kunskapsbaserade system/expertsystem. Värdering av några existerande verktyg" / "Knowledge Based Systems/Expert systems.
Evaluation of some existing tools". NBS-DATA seminarium, Oslo, 24-25 september 1987. (15 pp).
|
|
/6/
|
Johnson, M., 1999, "XML for the absolute beginner".
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-04-1999/jw-04-xml.html
|
|
/7/
|
Falk V, "LON i dagens Danmark". Dansk Automationsselskab.
|
|
/8/
|
Christiansson P. (2007) "ICT Enhanced Buildings Potentials", Proceedings 24th CIB W78 Conference "Bringing ICT knowledge to work". June 26 - 29 2007, Maribor, Slovenia. ISBN 978-961-248-033-2. (pp. 373-378).
Keywords: Intelligent buildings, ontology, service, future, functional systems.
|
6. Examination
[goto top]
Oral individual test based on 1-3 hour discussions a group on a mini project or exercises collection. Assessed with the grade "passed" or "failed" with internal
censor participation. There is no time for preparation.
Examination will take place in room 1.211, Fibigierstræde 16, Monday January 07,
2008. Examinator is Per Christiansson and censor Kjeld Svidt.
Registration no later than January 3, 2008, 12.00.
Kl. 8.15 Jesper Buskov
Kl. 8.30 Carsten Rune Jensen
Kl. 8.45 Henrik Sørensen
Kl. 9.00 Alexander Tsetsis
Kl. 9.15 Peter Brix
Kl. 9.30 Sune M. Rasmussen
Kl. 9.45 Jakob Lemming
Kl. 10.00 Morten Møllnitz
Kl. 10.15 Anders Dalum Nielsen
Kl. 10.30 Jens Møller Vestergaard
Kl. 10.45 Søren Krabbe
Kl. 11.00 Per Christensen
Kl. 11.15 Caroline B.E. Hansen
Kl. 11.30 Sonja Pedersen
The group exercises/miniproject reports and presentation at examination are if available presented here
- Group 3.101
- Group 3.108
- Group 3.110
7. Course Participants
[goto top]
7.1 Students
Buskov, Jesper Elgaard
Christensen, Jakob Lemming
Christensen, Per
Hansen, Caroline Birgitte Elnegaard
Jensen, Carsten Rune
Krabbe, Søren Hauge
Møllnitz, Morten
Nielsen, Anders Dalum Wagne
Pedersen, Sonja Dissing
Rasmussen, Sune Mejlsing
Sørensen, Henrik
Tsetsis, Alexandros Nikolaos
Vestergard, Jens Møller
Brix , Peter
3.101
Project with KUBEN company.

Buskov
Jesper Elgaard
|

Jensen
Carsten Rune
|

Sørensen
Henrik
|

Tsetsis
Alexandros Nikolaos
|

Brix
Peter
|
3.108
Project with Engaard company.

Christensen
Jakob Lemming
|

Møllnitz
Morten
|

Nielsen
Anders Dalum Wagne
|

Rasmussen
Sune Mejlsing
|

Vestergard
Jens Møller
|
3.110
Project with NIRAS and Smith Hammer Lassen companies.

Christensen
Per
|

Hansen, Caroline
Birgitte Elnegaard
|

Krabbe
Søren Hauge
|

Pedersen
Sonja Dissing
|
7.2 Teachers
Prof Per Christiansson (course responsible).
Civ.eng. Kristian Birch Sørensen (PhD student)
8. Lecture Scheme
[goto top]
1
Wednesday September 12, 2007
08.15-12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
(Per Christiansson)
|
|
World-Models-Systems
We explain some basic concepts and make definitions; systems, ontologies, conceptual models, data models, ICT, Building Information Models BIM, IDM, IFC Model views, and classifications.
Why and how ICT have been introduced in the building processes during the
latest decades (building processes, ICT system examples and properties, development driving forces, virtual organisations).
Building product and process models are explained and exemplified as well as
relevant knowledge management issues including new ways to handle information containers in local to global networks.
|
|
Literature
/1/
Exercise A
|
2
Monday September 17, 2007
08.15-12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
(Per Christiansson)
|
|
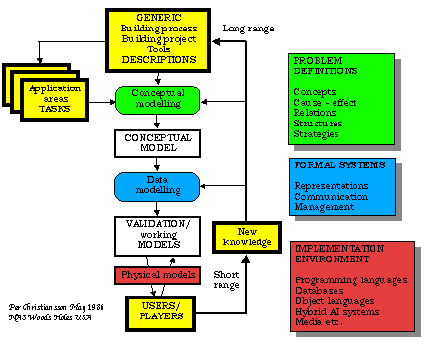
Conceptual Modelling
Different conceptual modelling methods may be used to describe functional systems of the building process.
Focus in this lecture is on Rich Pictures, IDEF0, SADT, Entity-Relationship, UML, and partly Contextual Design methods.
Business and technical services are explained and exemplified.
|
|
Literature
/2/,/3/
Exercise B
|
|
3
Wednesday September 19, 2007.
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.211
Aalborg University.
08.15-12.00
(Kristian Birch Sørensen,
Per Christiansson)
|
|
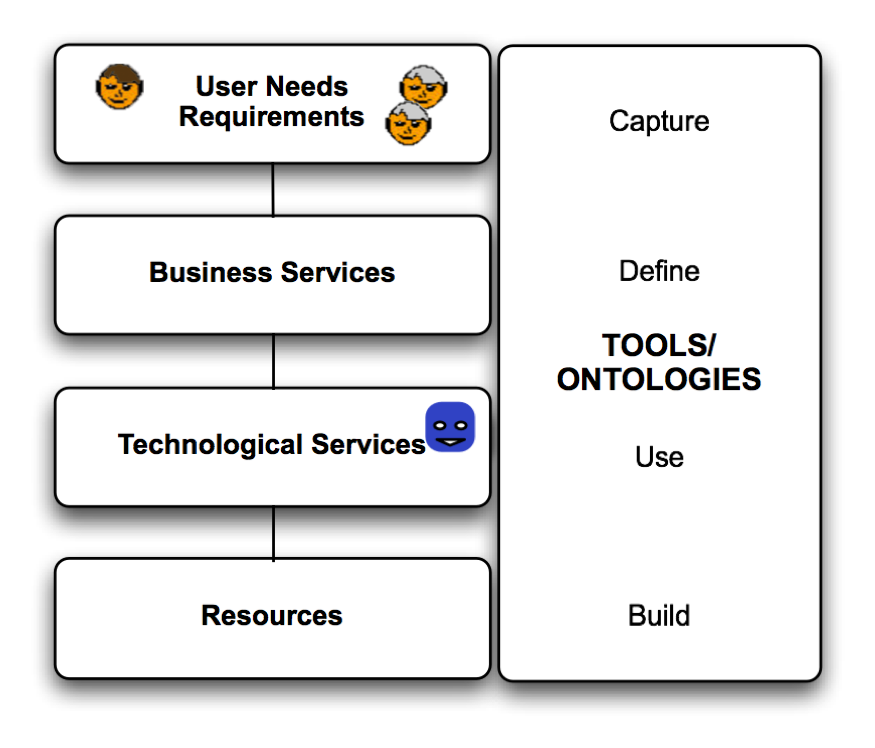
ICT Tools in Practice
Practical examples are presented, explained and analysed in the area of
relations between virtual building models and physical buildings during the whole building process and how these relations can be estqblisehed and maintained.
|
|
Literature
Exercise C
|
|
4
Wednesday September 26, 2007.
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.211
Aalborg University
08.15-12.00
(Per Christiansson)
|
|
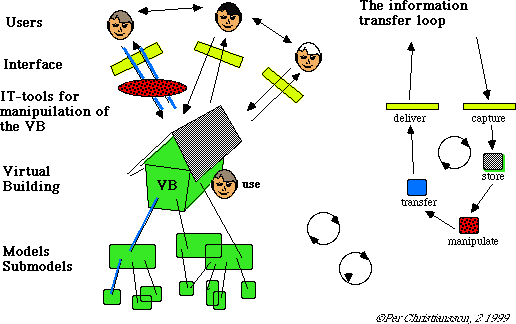
Knowledge Representations
We will look at different ways to transfer conceptual models to more structured data models that can be implemented and accessed through different knowledge representations implemented in digital computer systems.
|
|
Literature
/5/
Exercise D
|
|
5-6-7
Wednesday October 2, 2007.
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.201
Aalborg University.
13.00-16.30
(Per Christiansson)
Tuesday October 10, 2007.
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.211
Aalborg University.
08.15-12.00
(Per Christiansson)
Tuesday October 23, 2007.
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.101
Aalborg University.
12.30-16.30
(Per Christiansson)
|
|
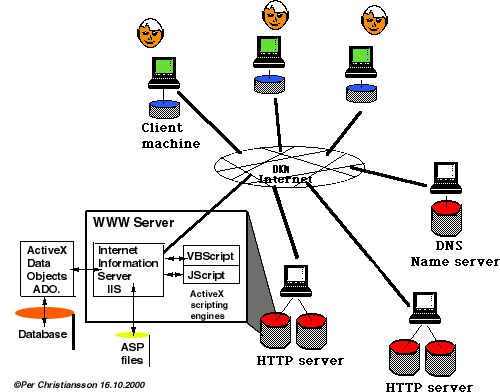
Relational Databases modelling and WWW access.
Relational databases is and will be an very important information container
for building process and product information.
We will learn how to design and imnplement a relational database as well as
learn about the principles and methods behind connecting databases to web browsers.
((Byggeweb))
|
|
Literature
/4/
Exercise E
|
8-9
Tuesday October 30, 2006
12.15-16.30
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.101
Aalborg University
Wednesday November 1, 2006
12.30-16.30
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.201
Aalborg University
(Per Christiansson)
|
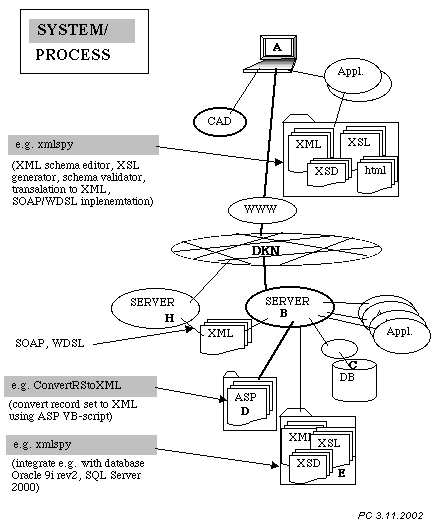
|
THE SEMANTIC WEB
These two lectures and exercises deals with the nex generation
knowledge representations in form of hypertext on the WWW, namely
Semantic Web.
"The Semantic Web is an extension of the current web in which information is given well-defined meaning, better enabling computers and people to work in cooperation."
[Tim Berners-Lee, James Hendler, Ora Lassila, The Semantic Web, Scientific American, May 2001].
|
|
Literature
/6/,
Exercise F
|
10
Tuesday November 6, 2006
12.30-16.30
Fibigerstræde 16,
room 1.101
Aalborg University
(Per Christiansson)
|
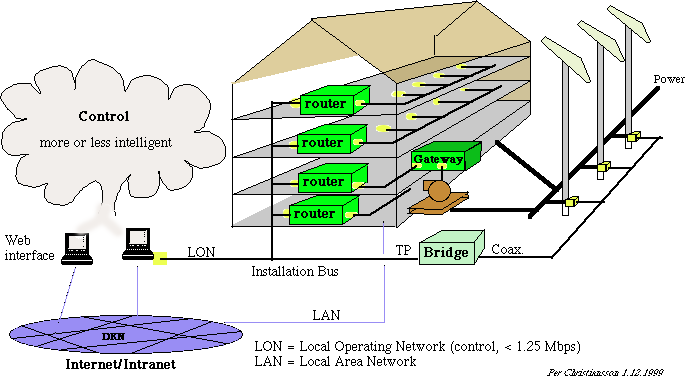
|
10. THE DIGITAL CITY AND SOCIETY.
THE INTELLIGENT BUILDING
Information technology,IT, will cause a paradigm shift in
our society from the art of writing, printing to the art
of communication.
In the same way as the car highly influenced the physical
design of our society IT will higly influence the forming
of the global villages.
We will investigate exisiting and expected infrastructures,
systems, and services in the intelligent buildings and digital cities,
and how they can be designed, modelled, and implemented.
|
|
Literature
/7/, /8/
Exercise G
|
|







