|
Education within IT in the Buildning Process
IT in the Building Process. Background
IT (computer support) was introduced during the 1960s in the building
process (calculations) by structural engineers. Since then the islands of automation according to figure 1 have slowly been growing and the gap between them easier to travers.
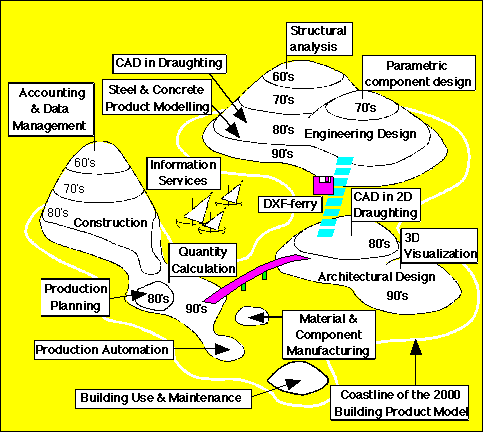
Figure 1. Islands of automation within the Building process (after Matti Hannus and Pär Sill'en, VTT, Finland)
Isolated digital islands have been created for design (2D/3D Cad, visualization, engineering calculations), construction (quantity take off, resource management), maintenance/use (hire administration, facility management), and resource supply (components/material databases). To this we shall add access to external vendor product information, regulations, and community information.
IT causes great changes that affect work content, team work and collaboration, project organisation, business and trading, building product and process descriptions (models) and ICT (Information and Communication) based tools. Which changes are relevant for the building sector? Of course we can out-source some competencies and work but also form strategic coalitions in new ways.
The complex project organization of the building industry together with higher international involvement will take great advantage of the future advanced ICT tools. The actual products will themselves also contain embedded and integrated IT support (Intelligent and responsive buildings). The building process will be more integrated, and suppoprted by (often redundant) product/process models. Information produced during the whole building project will to a higher degree support the maintenance and use of he final buildings and provide subsequent experience data.
The multimedia and virtual reality properties of the interfaces to the computer models of the building process and products will improve all the building process participants way to communicate and collaborate in distributed virtual collaboration spaces less constrained by time and geographic positioning.
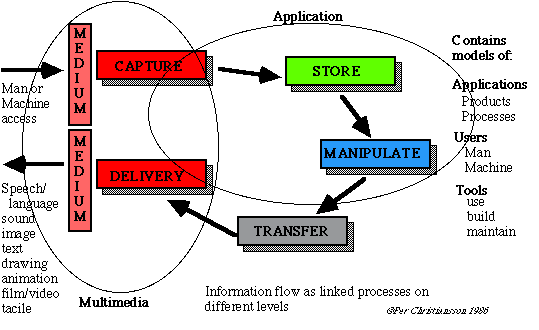
Figure 3. ICT (Information and Communication Technology) may be defined as the technology to support capture, storage, manipulation, communication and delivery of information on different application levels (from macro to micro scale)
The implementation in the building process has been rather slow due to
- the building process is one of the most complex and less formalized applied processes (short series of products, changing participants from project to project, changing production sites, cultural differences).
- Building process actors using different ICT tools, languages and model formalisms.
- Rich spectrum of user interfaces with different characteristics.
- Very cross scientific domain.
- Too little focus on building up it's own ICT competences (the out-sourcing trend diminishes due to risk of loosen company business strategic knowledge)
- Low client understanding that IT pays back (better early decisions in alternative solutions, higher quality and better documented end products.
Building Process Needs
There is now and in the future building industry a great need for persons who can take active part in specification, design, implementation, and evaluation of tomorrows building process support systems. A broad view and insight into the complex building process together with a broad and in some key areas deep knowledge into existing and coming ICT tools are required in combination.
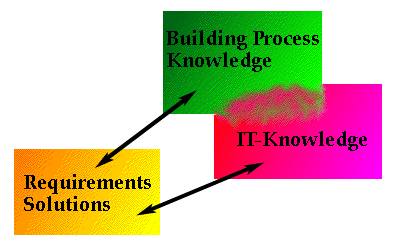
Figure 2.
Builders must know some basic IT to be able to formulate requirements on and participate in the design and implementation of tomorrows building process ICT-tools.
The IT community cannot (should not) by themselves build
tomorrows AEC tools.
We will through realistic simulations be able to get a much better support also as we make important decisions in the very early requirements formulation phase of the design process. We will increase our competence in specifying, designing, purchasing, building and maintaining the company IT systems. There will be increased need to formulate IT strategies to support the ongoing change process caused by design and introduction of new ICT supported tools.
Building Industry needs
- User needs and requirements formulation
- Participation in system design, evaluation and usability testing
- Specification and design of new User Environment
- User Interface design
- System interoperability and Web implications consideration
- New ICT tools design (using meta tools)
- Formulation of change and ICT strategies
- Specification, building and handling of Virtual Building models
- Global competitiveness success
- Increased effectivity and efficiency
IT-BUILDING STATUS AT INSTITUTE 6
Introduction
Since spring 1998 courses have been created with no extra development time set aside for an area with very little learning/teaching material. Also efforts have been put into enhancing AAU pedagogic methods with IT -support. Deliberately courses have had a broad focus with later possibilities for diffusion into more specialized courses to give IT a stronger position in the i6 curricula with synergy in A&D and Master of IT educations.
Goals
The overall goals with introducing IT in the Civil Engineering curricula are
- Students should understand overall implications of working with digital information (on personal, team, project, and company levels) and the properties of logic information containers properties and building product- and process models.
- Students should understand the ongoing change processes caused by ICT introduction. This requires a holistic and broad view on the building process and the surrounding world.
- Studensts should be able to actively participate in the design of nest generation digital building process environments and ICT tools.
- Students shall acquire deep knowledge within certain areas on design and adaptation of advanced ICT-tools as well as the relations between building process applications and ICT.
- Students shall be trained in and have deep knowledge in how IT can serve to integrate competences (also outside the engineering domain) and artifacts in the building process and how knowledge can be efficiently captured and transferred.
It is not enough for the students to acquire surface knowledge about tools handling without deep understanding of underlying phenomena, methods and theories. The risk is obvious that the civil engineers and Danish companies then will have problems to compete with foreign undertakings on a global work market. The project organised problem based learning paradigm utilized at Aalborg University gives the student good abilities to solve problems and work in groups but there is a risk for non effective learning due to repetitive routine project work.
Figure 4 outlines the overall knowledge domains which should be covered in the education.
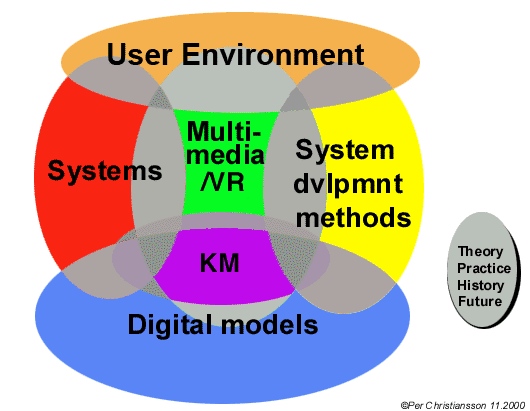
Figure 4: Overall education domains across which courses are defined.
Future development.
- Stage 1: finished now (introducing IT on broad with holistic approach)
- Stage 2: introduction of Virtual Building and User Environment Design courses at the Building Management (Byggeledelse) education
- Stage 3: re-definition of ICT-construction SE and PE courses establishing ICT as one of the fundamental competence areas with possibilities for late specialization (started).
- Stage 4: Closer integration of IT sub areas with existing building science courses. Possible specialization in 'Building Informatics'.
Courses given by the 'IT in Civil Engineering' group
B and BL line (Byg og Byggeledelse)
Department of 'Building Technology and Structural Engineering' (i6) introduced spring 1998 the first
course dedicated to IT 'IT in the Building Process'.
This was and still is a PE (Project Unit) course
with goal 'To give an broad overall understanding of IT use in the building process in historic, present and future perspectives' with special emphasis on knowledge management, relational databases, communication support,
multimedia web interfaces, and group project webs. The course mainly supports the project work in students
designing and implementing project webs to support their own collaboration, communication with teachers and
the final project presentation.
The project sem6 'IT in the Building Process' webs from 1998- are available at http://it.civil.auc.dk/it/educatuion/. Student projects webs and project reports from other courses are found under respective
course description on the web as well as lecture notes and references to other learning material.
The 'IT in Civil Engineering' group have developed more than 10 different courses described at http://it.civil.auc.dk/it/education/.
The Building Management education courses content are described through figures 5 and 6.
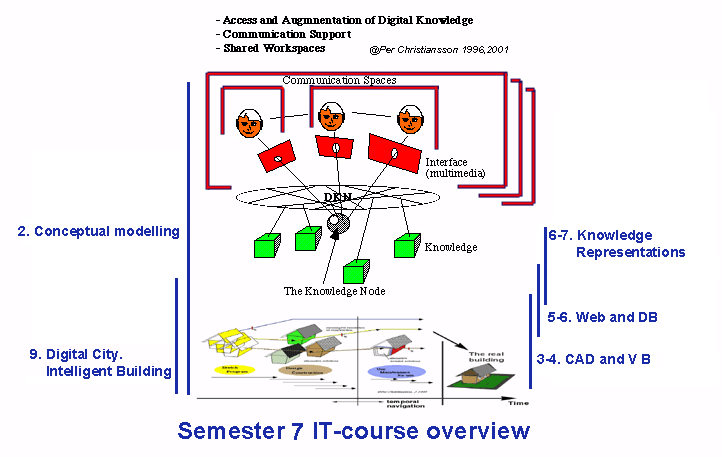
Figure 5.
ICT Tools. Virtual Building course at semester 7 Building Management.
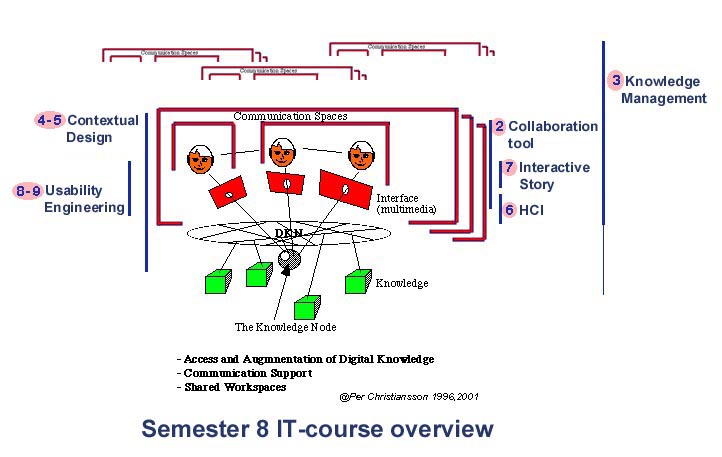
Figure 6.
ICT Tools. Multimdedia & Knowledge Management (Computerstøttet samarbejdet) at semester 8 Building Management.
Courses given at MII (open Master of Industrial IT)
- Human Computer Interaction/Grafiske brugergrænseflader . MII-1. Semester 1 (1M, PE)
- Teknologistøttet Samarbejde - CSCW - MII-1. Semester 1 (1M, PE)
- Multimedia interface design and Computer Collaborative Work - MII-2. Semester 3 (2M, PE)
- Knowledge Management within Companies and Projects MII-2. Semester 3 (2M, SE)
- Intelligent Buildings and the Digital City - IBD. Semester 5 (2M. SE)
- Virtual Buildings. MII-3. Semester 5 (2M,PE)
- Building simulations . MII-3. Semester 5 (2M, PE)
Course proposals for B and BL lines
The Building Informatics domain
As a basis for further discussion on the interaction between ICT related courses and other civil engineering education courses and projects, figure 7 is presented.
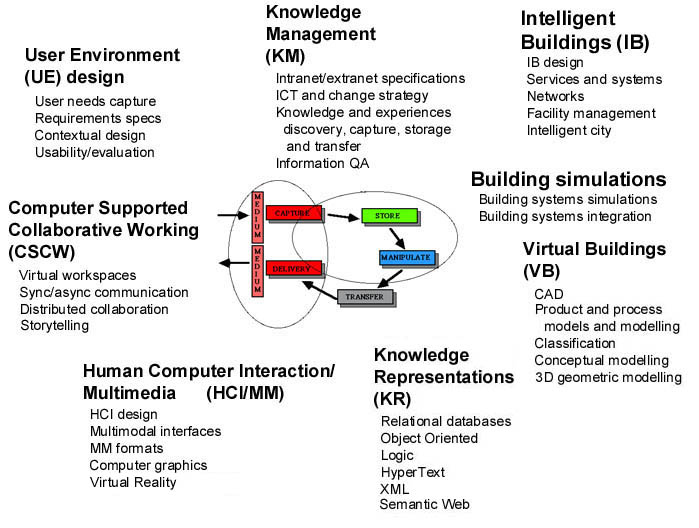
Figure 7.
Building informatics related areas. We give courses at Master of IT and Building Management educations in many of the sketched areas.
New course structure
We propose as the next stage in developing the Building Informatics (Bygningsinformatik) education at the Bx-lines AAU the following main knowledge domains to be covered
- Basic ICT understanding
- Building Product/Process Modeling (Modellering af bygninger)
- Databases and knowledge representations
- ICT supported collaboration
The areas will be covered by existing and new courses according to the scheme below.
See also Danish version of the below content.
COURSE NAME
PLACEMENT/TYPE
|
GOAL/CONTENT
|
Basic Building ICT,
(Grundläggende IKT förståelse)
Basis, semester 1
2M, Free Study Activity
|
Goal. The course will mediate basic knowledge about information and communication technology (ICT) tools usage in the building process
Content
- ICT tools used in the building industry - history, present, future
- Database intro and digital information containers
- Project webs and collaboration
- Multimedia interface properties
- (Web)client-server and peer-to-peer technologies
- Communication and integration standards and protocols
- XML and meta languages
- Webservices.
- Tools for graphic editing
- Techniques and methods for designing and implementing world wide web based multimedia presentations.
Exercises/mini projects:
Digital presentations and reporting.
Project web and building process ICT tools properties and structure
|
Computer Aided Design basics,
(Cad basics)
Basis semester 2
2M, Free Study Activity
|
Goal.The course will mediate knowledge about concepts, techniques and methods for computer aided design (CAD) tools.
Content
- Autocad functionality and tools
- 3D wired, faces and solid models
- 3D Studio functionality and tools
- Possibilities, limitations and development trends
Exercises/mini projects:
......
|
Building Product/Process Models,
(Bygningsmodeller)
Semester 4
1M, SE
|
Goal.The course will mediate knowledge about concepts, techniques and methods for building models of the building products and processes and to give understanding of how these models can be used in trhe design work.
Content
- CAD systems properties (ADT, Revit, ArchiCad)
- Models of buildings in Cad systems
- IFC, International Foundation Classes
- Work on common building product models, modelservers
- Cad system interoperability
Exercises/mini projects:
......
|
Databases and Knowledge Representations,
(Databaser)
Semester 5
1M, SE
|
Goal.
The course will mediate knowledge about concepts, techniques and methods for design, implemenation and use of relational databases in the building process as well as mediate understanding
what digital knowledge representations can be used for different building process contexts.
Content
- Theoretical fundaments of relational databases
- Conceptual modelling af relational databases
- Entity-Relationship (E-R) models
- Normalisation
- Structured Query Language, SQL
- Other knowledge representation in the building process
|
ICT Supported Collaboration,
(IKT støttet samarbejde)
Semester 6
1M, PE/SE
|
Goal.
The course will mediate knowledge about concepts, techniques and properties for ICT tools to
support collaboration and communication in virtual and physical environments
Content.
- Principles and technologies for computer supported collaboration, decision support and knowledge management.
- Properties of ICT tools for collaboration. Collaboration in Virtual Reality environments.
- Multimedia (MM) and Human Computer Interaction (HCI) history and development. Properties for MM communication channels. Standards and protocols to support HCI and collaboration. Virtual Reality systems.
Exercises/mini projects:
.........
|
Virtual Buildings,
(Virtuelle Bygninger)
Semester 7
2M, SE
|
EXISTING
The goal of the 'IT in the Building Process - The Virtual Building' course is to mediate knowledge about fundamental concepts, technologies and methods to analyse and develop models which describes a building, the building process and the digital infrastructures from design to application as well as mediation of knowledge about how the future services, systems, and infrastructures for knowledge management can be built and integrated
Content
- Explaining Knowledge Management. Knowledge Management tools. Principles for meta-structuring in web based structures. Project webs. Properties of the next generation Semantic Web. (XML, RDF).
- Knowledge representations in practice.
- Web database integration.
- Existing classification systems and meta classification methodologies (XML-schema,RDF).
- Conceptual and data modelling techniques.
- Acquisition and storage of building process data. Design and development of services for knowledge transfer and knowledge management.
- Introduction to conceptual modelling methods and languages.
- Building Product Models in perspective.
- Building applications supported by product models.
- Building 3D models for the Web (Virtual reality mark-up language - VRML, and Cult3D).
- Future structures of virtual building models.
- International Foundation Classes, IFC.
- IT infra structures and intelligent buildings
|
User Environment Design/
Work Place Design
Virtual Work Places,
(Virtuelle arbejdsmiljøer)
Semester 8
2M, SE
|
EXCISTING, with new name, slightly exchanged content
The goal of the 'IT in the Building Process - IT-tools' course is to mediate understanding of principles, methods and technologies for design and evaluation of user environments for computer supported interaction and collaboration as well as team work and knowledge transfer.
Content
- Design of User Environments (UE). Principles, guidelines, the Contextual Design method, incremental prototyping. User models. Usability engineering and evaluation of user environments.
- Multimedia (MM) design and Human Computer Interaction (HCI).
- Digital video and interactive story telling.
- Web-based 3D models.
|
Total number of modules
- B: 2M+2M Frees Study activity. 1M+1M SE, 1M PE. Total= 7M
- B+BL: 7M + 2M SE + 2M SE = 11 M SE
|
Further courses given at
- Master if IT education
- A&D eduaction
|
REFERENCES
/1/ "The Future of Engineering Software". slides/future_eng_software.html
From http://www.cadsociety.org/summit/Whitepaper_Article.htm and Computer Graphics World. February 2000 (pp. 23-24).
/2/ "Bygge/Bolig - en erhvervsanalyse". Erhvervsfremme Styrelsen february 2000. slides/bygge_bolig_efs_2000.html
Christiansson et.al., 2000, "Forslag til instituttets strategiplan 2000-2005". 21 augusti 2000. (21 pages). pages 12-13 IT group , chapter 5.4 page 14 on 'integrated design'.
http://it.civil.auc.dk/it/reports/r_strategiplan_21_8_2000.pdf
|
|















