|
IT Tools - Multimedia & Knowledge Management
IT i Civilingeniørspeciale i Byggeledelse/IT in Building Management. 2003
1. Background
[goto top]
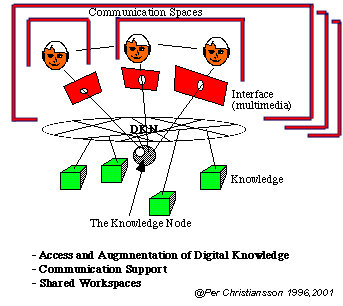
Since the introduction of the world wide web (WWW) and standardisation of Internet services and communication protocols we can see a huge shift in the way we communicate, collaborate and handle digital knowledge. In the semester 7 course we focused on models and representations of building products and processes. In this course we take an end user perspective on how ICT tools can support collaboration, communication and access to Internet based computer resources.
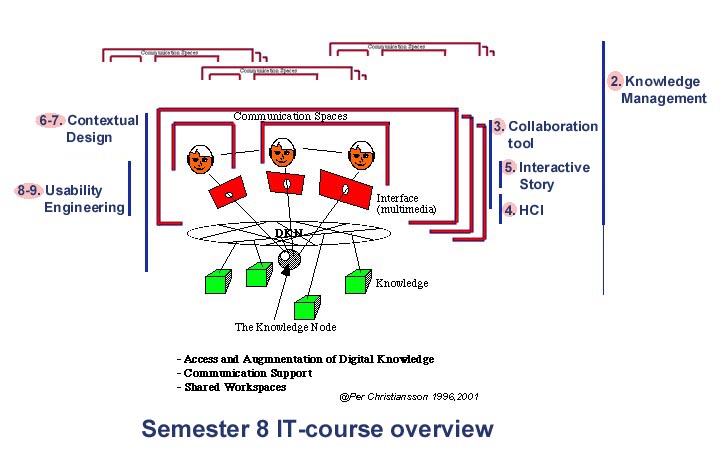
The anticipated ICT tools are only partly developed and must be designed tested and implemented in close collaboration with the building process end users. This requires that civil engineers get a deeper understanding of some knowledge domains that up till now only has been partly covered in the civil engineering curricula.
The ICT will strongly influence how we take advantage of and interact with the computer resources
- information storage and interaction media will be more separated (paper is both)
- it will be easier to adapt human computer interaction to user needs and usage context (multimedia, model access etc.)
- human collaboration, team work and communication modes will be developed and partly changed
- collaboration work spaces will get a added virtual dimension being less dependent of the physical room.
The mutual influence between practice and ICT progress is necessary to maintain. Civil engineers must posses both general and some specialised ICT related knowledge to be able to specify and participate in the development of new ICT tools and to be pro-active in the process of changing work routines and company and project organisation.
This course aims at providing general knowledge on how new user environments (UE) can be designed and implemented as well as deeper knowledge in certain key areas such as human computer interaction support, virtual work spaces, user driven user environment (UE) design, and user requirements capture and usability engineering.
2. Goal
[goto top]
The goal of the 'IT in the Building Process - IT-tools' course is to mediate understanding of methods and technologies for multimedia human machine interface design, computer supported collaborative work, graphical decision support and, as well as mediation of knowledge about how the future services, systems, and infrastructures for information transfer (knowledge management) can be built and integrated.
3. Volume/Placement
[goto top]
This 2 modules course is one of 2 with emphasis on IT during the semester 8 Master of IT in Building Management education
(calendar).
4. Content
[goto top]
Explaining Knowledge Management. Knowledge Management tools. Principles for meta-structuring in web based structures. Properties of the next generation Semantic Web.
Principles and technologies for computer supported collaboration, decision support and competence co-operation. Collaboration in Virtual Reality environments.
Interactive digital film tools and interactive story telling
Multimedia, MM, and Human Computer Interaction (HCI) history and development. MM communication channels properties. Standards and protocols to support HCI and collaboration.. Virtual Reality systems. Building 3D models for the Web (Virtual reality mark-up language - VRML, and Cult3D).
Design of User Environments, multimedia and HCI tools. Principles, guide-lines, the Contextual design method, authoring tools, incremental prototyping. User models (competencies profiles, languages, digital agents and agent co-operation. Usability engineering and testing of HCI tools
5. Learning Material
[goto top]
The course content is delivered through the lectures, reading of literatur , and exercises/miniproject. It is impossible to find a set of literature that covers the course content completely. The lectures are supported by lecture slides available on the course web site. The slides with emphasized titles in the navigation bar has the same status as course literature (though not eventual references on the slide).
References to further reading is found in the lecture notes.
The coarse literature consists of both Lecture Slides and literature according to the list below.
The 'IT in Civil Engineering' site (http://it.civil.auc.dk/) also gives access to
previous years courses and if applicable mini projects. You reach it from the top of this page.
5.1 Lectures
[goto top]
The lectures are accessed from the lecture scheme below.
Each lecture has a easy to navigate slide bar and an opening slide with
short content description, questions for self assessment, references to the literature according to the literure list below and proposals for further reading.
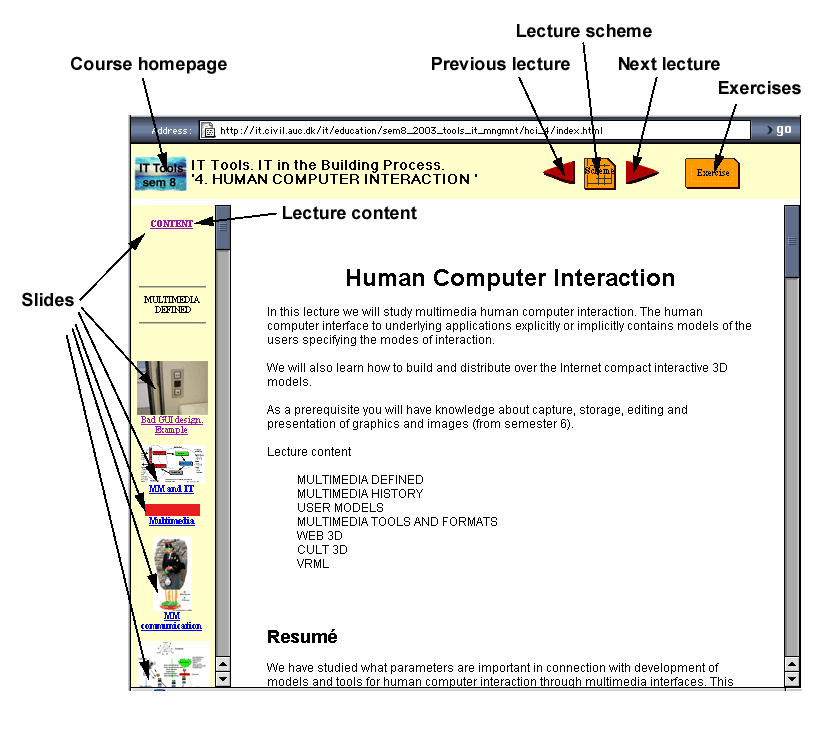
5.2 Exercises/Mini-project
[goto top]
The exercies are accessed from the lecture scheme below.
The exercices may well take use cases from the ongoing semester project or even be contained in a mini-project defined by the group.
The following domains will be covered during the miniproject
- contextual design methodology
- human computer interaction, HCI, and user interface design
- usability testing
- handling multimedia content
- interactive story telling
- (distributed collaborative work spaces and distributed learning)
-
5.3 Software
[goto top]
The following ICT, Information and Communication tools, are available during exercises/minproject activity. (those marked with * only at the Media Lab at institute 6)
- 3DStudio Viz to produce an interactive WWW-accessible VRML model (*)
- 3DStudio Max and 3dCult to produce an interactive 3dCult model (*)
- Cult3D modeller
- ArchiCad to produce VRML models
- Macromedia Director 8 (*)
- QuckTime VR interactive image software
- Adobe Premier to produce web accessible streaming video (*)
- Adobe Photoshop for image editing (*)
- Adobe Acrobat Distiller and Exchange to produce interactive PDF documents
- Groove, Netmeeting, and Yahoo Messanger to establish shared workspaces
-
5.4 Literature
[goto top]
|
/1/
|
Christiansson, P, 1998, " Using Knowledge Nodes for Knowledge Discovery
and Data Mining." Published in: Lecture Notes i Artificial Intelligence 1454. Ian Smith (Ed.).
"Artificial Intelligence in Structural Engineering. Information Technology for
Design, Collaboration, Maintenence, and Monitoring." Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
1998. (pp. 48-59).
http://it.civil.auc.dk/it/reports/ascona_98/ascona98.html
|
|
/2/
|
Christiansson P, 1997, "Experiences from developing a Building Maintenance Knowledge Node."
CIB Proceedings W78 Workshop, Cairns 9 - 11 July 1997, 'Information Technology Support for Construction'
Process Re-Engineering, IT-CPR-97'. Cairns, Australia July 9-11, 1997. (pp.89-101).
|
|
/3/
|
Christiansson P, 2001, "Experiences from Using Internet Based Collaboration Tools". 'Konference om Arkitekturforskning og IT'. Proceedings Conference on Architectural Research and Information Technology. Nordic Association for Architectural Research. Arkitektskolen i Aarhus 27.-29. april 2001. (pp. 103-112).
KEYWORDS: Virtual reality, collaborative work, ICT tools, design, intelligent buildings, knowledge transfer.
|
|
/4/
|
Collaborative Mixed Reality Mark Billinghurst, Hirokazu Kato
Human Interface Technology Laboratory. University of Washington
http://www.hitl.washington.edu/publications/r-98-36/
|
|
/5/
|
Nielsen A, 1998, "VRML programs for Room Ventilation Applications", Paper for ROOMVENT 98, Stockholm, Sweden VRML Programs for Room Ventilation Applications, Paper no 95, Indoor Environmental Engineering, Dept. of Building Technology and Structural Engineering, Aalborg University, December 1998, ISSN 1395-7953 R9846
|
|
/6/
|
Cult3D education material. Cycore 2001. (123 pp.)
|
|
/7/
|
Svendsen J. O. S., 2001, "Video på din PC". IDG Forlag, Valby (pp. 79).
[Pages 23-27, chapter 4 'Historiefortælling'].
[Chapter 5 'Redigeringens fortræffeligheder pp. 28-42, chapter 6 'OPtageteknik på 20 minutter' pp. 42-54].
|
|
/8/
|
Dreijer N, 2002, "Sådan virker et digitalt videokamera". Ingeniøren, fredag 22.3.02, Nr. 12. (pp. 8-9)
|
|
/9/
|
Mohr H L, 2001, "De nye medieformater", PCWorld, nr 22. (pp. 73, 74, 76)
|
|
/10/
|
Christiansson P, Skjærbæk J O, Svidt K, Aaholm R, 2000. " User Requirements Formulations and Human Computer Interface Design in the Divercity project. Context and methods." EU project
Divercity. (Draft report, Dec 17, 2000. 31 pages).
http://it.civil.auc.dk/it/reports/r_divercity_user_req_2000.pdf
|
|
/11/
|
Christiansson, P, 2001, "Capture of user requirements and structuring of collaborative VR environments". AVR II & CONVR 2001. Conference on Applied Virtual Reality in Engineering & Construction Applications of Virtual Reality. (eds: O. Tullberg, N. Dawood, M. Connell. 201 pp.)
Gothenburg October 4-5, 2001. (pp. 1-17).
|
|
/12a/
|
Preece J, Rogers Yvonne, Helen Rogers, 2002, "Interaction Design - beyond human-computer interacikon". John Wiley & Sons, New York (519 pp). (Amazon Books, 56 US dollars). http://www.id-book.com/. (page 295-306, 313-315)
(pp. 344, 347-358)
|
|
/12b/
|
Preece J, Rogers Yvonne, Helen Rogers, 2002, "Interaction Design - beyond human-computer interacikon". John Wiley & Sons, New York (519 pp). (Amazon Books, 56 US dollars). http://www.id-book.com/. (pp. 344 - 358)
|
|
/13/
|
Faulkner Xristine, 2000, "Usability Engineering". MacMillan Press, New York (244 pp.). (EXTRACTS: pp. 21-28 'Usability - know the user', pp. 157-160 'Cooperative Evaluation', pp. 188-192 'Usability heuristics'.)
(http://www.palgrave.com/science/computing/faulkner/)
|
|
/14/
|
Svidt K, Bjerg B, 2002:
"Visualisation of CFD Results in a Virtual Reality Environment".
Proceedings of ROOMVENT 2002, 8th International Conference on Air Distribution in Rooms, Copenhagen, Denmark, September 2002 pp 77 - 80.
KEYWORDS: CFD, Virtual Reality, Immersive Environment, Visualisation
|
6. Examination
[goto top]
Oral test based on 1-3 hour discussions a group on a mini project or exercises collection. Assessed with the grade "passed" or "failed" with internal
censor participation.
Examination will take place at Fib. 16, Tuesday June 3,
2003, at 09.00 (Group 2.121), 10.00 (Group 2.124), and 11.00 (Group 2.126) . Examinators are Per Christiansson and Kjeld Svidt, censor Claus Topp.
The group miniproject reports and presentation at examination are presented
here
7. Course Participants
[goto top]
7.1 Students
The students come from semester 7 of the civil engineering
Building Management program.
7.2 Teachers
Prof Per Christiansson (course responsible) , Asst. Prof. Kjeld Svidt.
8. Lecture Scheme
[goto top]
1
Friday March 11, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
|
|
SETTING THE SCENE
IT as communication support.
Human computer communication system form and function
Information content and format
User environment design
How to convey the message
Available IT/Multimedia tools
|
|
Literature
|
2
Friday March 11, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
|
|
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
We explain why Knowledge Management issues are
important to take into consideration as we design and implement
the digitally supported user environements. What models
(organisation, project, user etc.)
are influenced and what ICT tools are available or even missing
as focus on knowledge management is increased.
|
|
Literature
/1/, /2/
|
3
Friday March 11, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
|

|
COLLABORATION TOOLS
Principles and technologies for computer supported collaboration
and competence co-operation.
Properties of IT-tools for collaboration.
|
|
Literature
/3/, /4/, /14/
|
4
Friday March 11, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
|
|
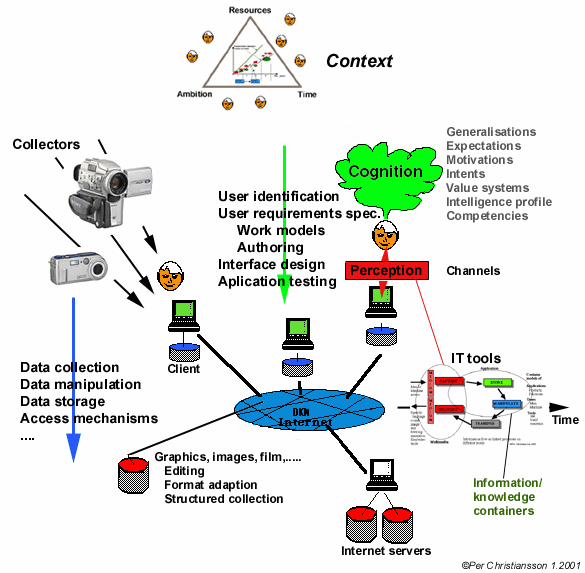
HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION
In this lecture we will study multimedia human
computer interaction. The human computer interface
to underlying applications explicitly or implicitly contains
models of the users specifying the modes of interaction.
We will also learn how to build and distribute over the Internet compact interactive 3D models.
As a prerequisite you will have knowledge about
capture, storage, editing and presentation of graphics and images
(from semester 6).
|
|
Literature
/5/, /6/
|
5
Friday March 11, 2003
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
|
|
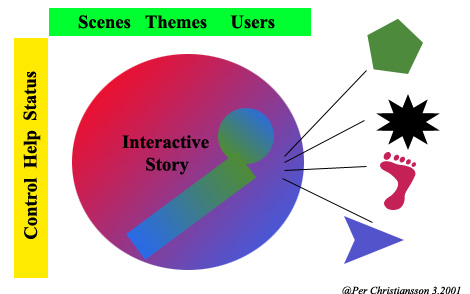
INTERACTIVE STORY TELLING AND DIGITAL VIDEO
It may be useful to regard a web presentation as a story. You have something you want to tell the 'reader'. It could be something about what services your company may offer, best practice for your intranet/projectweb, or a story to your employees on possible changes in you company to raise quality in services and working environments. Story telling is increasingly used by companies to deliver important information.
We will take starting point in linear story telling using video and move to multimedia based presentations at the same time introducing interactive story telling. You have also get hands-on experience on methods and techniques to plan, capture, edit and include a video element in a web based presentation.
|
|
Literature
/7/, /8/, /9/
|
6-7
Thursday March 19, 2003.
12.30 - 16.15
Room 1.211
Thursday March 20, 2003.
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
|
|
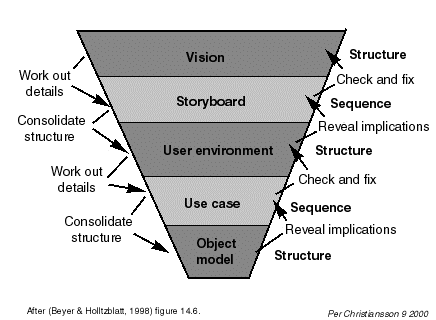
CONTEXTUAL DESIGN
We will during two lectures learn about the Contextual Design
methodology to incrementally capture user requirements and specifiy a
User Environment for accessing computer resources. We also make references to a parallel process with emphasis on the technical modelling and system implementation.
|
|
Literature
/10/, /11/, /12a/
|
8-9
Thursday April 3, 2003.
Thursday April 10, 2003.
8.15 -12.00
Fibigerstræde 14,
room 59
Aalborg University
|
|
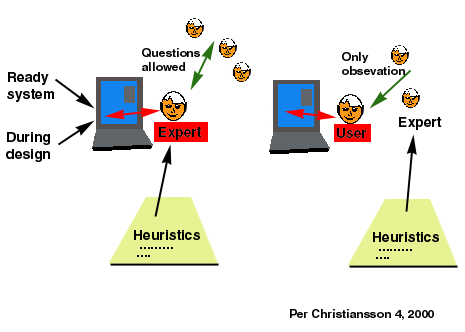
USABILITY ENGINEERING
During two lectures
we explore the field of Usability Engineering including
usability testing and evaluation of HCI tools and interfaces to
application systems. We also cover alternative methods to defining and building User Environments.
|
|
Literature
/12b/, /13/
|
10
Monday May 12, 2003.
14.00 -16.00
VRMediaLab,
Aalborg University
|

|
SPECIAL ISSUES
Visit to the VRMediaLab.
Exercises/Mini project follow-up
Special issues on request
|
|
Literature
|
[goto top]
|
|






