|
|
Exercise A on the relation between world-systems-models
Exercise B on conceptual modelling
Exercise C on ICT tools in practice
Exercise D on knowledge representations
Exercise E on database design and web access
Exercise F on meta structuring of information using XML and RDF
Exercise G on new services in digital cities and intelligent buildings
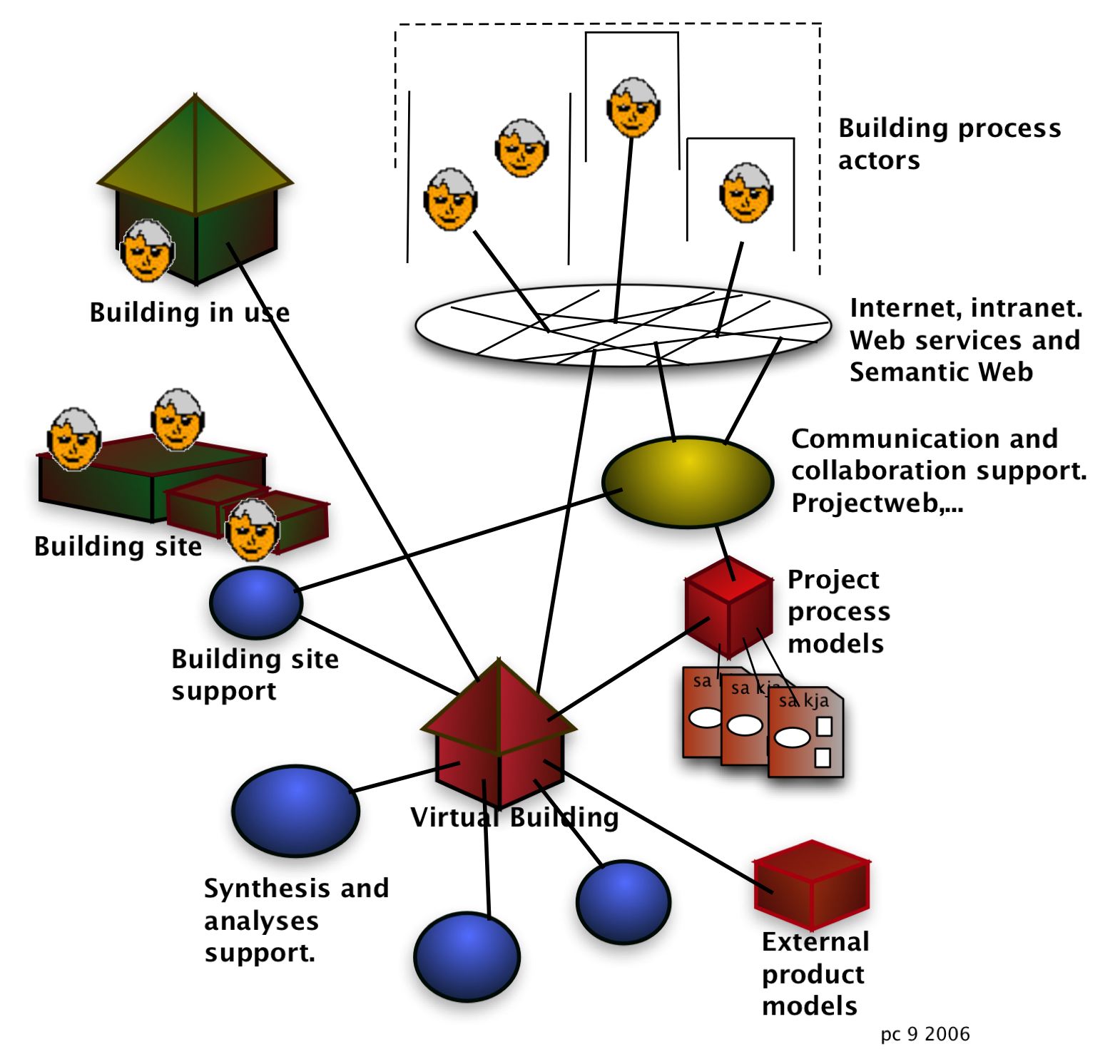
The course exercises uses modelling domains of this figure.
The students come from semester 6 of the civil engineering
program. (You can also take a look at the
exercise sem7 2005 notes,
exercise sem7 2004 notes,
exercise sem7 2003 notes,
exercise sem7 2002 notes,
exercise sem7 2001 notes,
exercise sem7 2000 notes,
exercise sem7 1999 notes)
Exercises shall be carried through and may also be part of a mini project.
The exercises may if possible be related to your semester project.
The four hour lecture/exercise follows the scheme
- 1 hour lecture
- 1 hour exercise in group
- 2 hours exercise results presentation and follow discussions
Here you can find some of the exercise work results
Exercise A on models and systems
[goto top]
List some possible functions and services that a client would wish for his building complex (choose an office building or an apartment house).
Indicate which building component systems that will be affected by respective function.
[exercise work results]
Exercise B on conceptual modelling
[goto top]
In connection with lecture "2. CONCEPTUAL MODELLING" you shall start
to develop conceptual models at high abstraction level
of your semester 7 project or part of functional system you sketched in exercise A. Also use the figure above to support your choise of system.
- Define the overall function(s) of the system under consideration. Use initial needs and wishes expressed by the client
- Try to give names on the system and it's subsystems.
- Choose the system and subsystems you intend to model, design, and implement.
- Start the modeling work by drawing rich picture conceptual models starting on top level.
- Draw a top level process model using IDEF0 diagram.
- Discuss what possible UML diagrams can be constructed during implementation.
[exercise work results]
Exercise C on ICT tools in practice
[goto top]
- List a catalog of ideas for new ICT-systems based on linking
virtual construction models with the real building.
- Group the ideas according to its intended users; design-team,
contractor, owner and end user.
- Choose your preferred idea and write and sketch a scenario for
it.
- Each group must prepare a short presentation of the ideas and
scenario.
A scenario is an analysis of challenges and future possibilities for development. The scenario will help us to communicate and gain insights in future developments. It should be as objective as possible taking into account evaluations and analyses of viable future ICT developments and organisational and work environment changes. The scenarios are stories and do not talk about specific technologies in depth but try to develop a story about what people must do in order to complete their task or goals.
[exercise work results]
Exercise D on Knowledge representations
[goto top]
Describe what representations you find appropriate to use in connection with ICT systems that support
- Virtual Building models
- Document handling
- Experience Capture
- Meeting notes
- your own suggestions....
[exercise work results]
Exercise E on database design and web access
[goto top]
In connection with lectures "5-7. WEB AND DATABASES" you shall design a small database and make it accessbile from the Internet (in your case from a local server on your student dommain).
- Design a relational database that based on a fictive building project can coordinate and store involved companies, persons, the person's competencies and documents related to a building project.
[You may also use the results from previous exercises or part of your semester project to make a conceptual design of the relational database.]
- The database should contain five or more related tables (e.g. companies-employees-competencies etc.)
- Implement the database using Microsoft Access.
- Test database access using the in built possibilities to make forms in Access.
- Document your design and database queries.
- Try-out how the SQL calls can be transferred to the database (in two or more html/ASP-files to access the database via a Internet Information Server (IIS) or Personal Web Server (PWS) from a web-browser).
- Use FTP to upload your ASP pages to the server. You can store the pages in the same directory as the database or in sub-directories. (The database 'building_db' is also available, http://192.168.125.51/building_db/ show asp and html/source files)
- You access your web pages at http://192.168.125.51/3120/X resp. http://192.168.125.51/3122/X where X= a,b,c,d,e,f or g. One for each person in the group.
- Name and place your database and asp-files at the server according to 3120/a/a.accdb etc.
- An example database and asp files are found at http://192.168.125.51/asp_example. You can download these, rename and revise them, and upload them to the your directory at the server.
You can access the
Use the DSN method to connect to the database (y=a,b, etc. x= 0 eller 2)
Set objConn = Server.CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
strConnection = "DSN=312x y;Database=y;"
strConnection = strConnection & "UID=312x;PWD=312x;"
objConn.Open strConnection
[exercise work results]
Exercise F on meta structuring of information using XML and RDF
[goto top]
In connection with lecture "7. KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATIONS (XML,HTML)"
you shall study how XML and related technologies can be used to store, validate and present data.
Part 1
- Filerne ex_e.xml, ex_e.xsd og ex_e.xslt gemmes lokalt på harddisken (vær opmærksom på filendelserne: .xml, .xsd, .xslt.)
- Via en tekst editor (fx WordPad da denne beholder formateringen) dannes et overblik over ex_.xml filen og der tilføjes en etage (storey) med min 2 spaces til bygning 1.
Gem XML filen i et nyt navn.
- Valider den nye XML fil med XML Skemaet ex_e.xsd via validatoren
http://www.exchangerxml.com/.
[or http://www.altova.com/products/xmlspy/graphical_xml_schema_editor.html]
- Via editoren foretages følgende ændringer i ex_e.xsd:
- Værdi i SpaceType skal være "entrance" i stedet for "communication".
- Der kan maks. være 2 etager i en bygning.
- Valider XML filen og foretag nødvendige ændringer i XML filen.
- XML dataene skal nu formateres til HTML via et stylesheet.
Indsæt i 2. linie af XML filen følgende: <?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="ex_e.xslt"?> og åben XML filen i en browser.
- Lav ændringer i ex_e.xslt filen, fx. ændring af farver, skrifttyper og formateringer.
- Dokumenter øvelsen via udsnit af koden samt skærmdumps.
Part 2
- Hent og installer editoren RDFedt
- Opbyg vha. RDFedt (eller tekst editor) en RDF beskrivelse om en fiktiv webressource (fx http://www.test.dk/dok1.pdf), der baseres på Dublin Core Element Set 1.1
Der skal indgå minimum 3 metadataelementer. [Eksempel]
- Valider RDF beskrivelsen med W3C's RDF Validator
- Dokumenter resultatet via skræmdumps og korte kommentarer til hvad der sker i koden
- Hvordan mener I at denne teknologi kan anvendes i byggebranchen. Drag fx sammenligninger med projektweb systemer, der blev omtalt tidligere.
- Hvilke processer i en virksomhed kan understøttes af teknologierne.
[exercise work results]
Exercise G on new services in digital cities and intelligent buildings
[goto top]
You shall in this exercise take the role of client advisor in the intelligent
building domain. The client will build a new office hotel or renovation of dwelling houses. You should produce
information to support the client in his formulation of (new types) ICT
supported services (based on user needs) and how these can be designed, implemented and used.
- list those intelligent building type of services you will present to the client (try to envision end-user needs)
- describe how some of these services could be implemented in the intelligent building
- present a tentative requirements list on IB supported functions and services in
the planned office.
- also describe how a IB design team could be composed
[exercise work results]
Questions Examples from lecture notes
World Models and Systems
- Give some examples on digital models we can build for the building process.
- Why do we build digital building process/product models?
- What is a digital Virtual Building model?
- Give some examples on services we can implement in an office intranet.
- How can digital models help us communicate with product/component manufacturer?
- What is ICT?
- Give some examples on how ICT is pushing us into the knowledge society.
Conceptual Modelling
- Why do we need top make conceptual models of our applications that we want to store in the computer systems as digital models?
- Draw a functional model graph of the following application - selection and ordering of windows for an office building with special regard to the communication with the window producer.
- Give examples on conceptual modelling methods and the corresponding application systems they are well suited to model.
- Describe over time different activities in ICT system design.
- ((Sketch work models (according to the Contextual Design method) for the internal structure and information flow on use of system for drawing and document handling on an office intranet.))
ICT tools in practice
- Give examples on some benefits we will obtain by linking virtual models with real objects in construction
- How can virtual buiding models and physical buildings be linked?
Knowledge Representations
- How can we represent knowledge in computers?
- Give some examples of computer stored knowledge representations/data models
and describe their properties and possible application domains.
- What do you mean characterizes a knowledge management system?
WEB and DATABASES
- What characterizes a relational database? (Explain the first three levels of relational database normalisation).
- What is Structured Query Language, SQL. Explain the 'select', 'from', and 'where' clauses.
- Explain how a database can be accessed from the Internet via a web browser
(using ODBC Open Database Connectivity).
The Semantic Web
- What is XML, XSL and XML schema?
- How can XML formatted data support application interoperability on WWW?
- What is the Semantic Web?
The Digital City and Intelligent Buildings
- Sketch an example on an intelligent building installation and services based on LON, Local Operating Network,
- Mention four important benefits using Intelligent Building
Installations.
- Which competences (and why) would you involve in design, build-up and operation/maintenance of
the intelligent building installations, IBI?
- Which types of services can be introduced in the digital city information
networks?
- Discuss capacity and other properties of different networking
technologies that can be used in the digital city.
- Which competences (and why) would you involve in design, build-up, and operation/maintenance of
the digital city?
|
|





