What is Internet? Client-server, http, ftp, email protocols.
Web basics. Associative thinking. Hypertext. Presentation media.
|
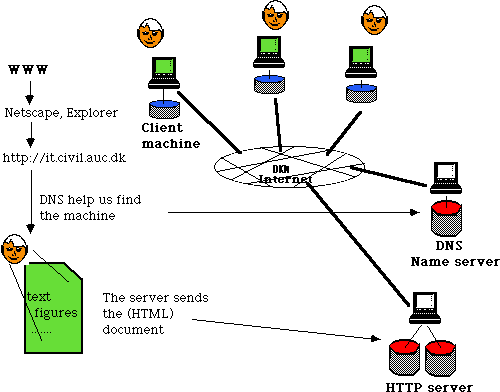
Figure 1
- The World Wide Web let us easily handle documents on
the Internet.
- Your machine contain the client software (Netscape, Explorer). The server contain HTML-documents (HyperText Markup Language) which
can be reached on the Internet.
- The client software (Netscape) can change the size of the www-document text, (e.g. header texts).
- Protocols HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), EMAIL. HTTP is the newest from roughly 1992.
|
|
|
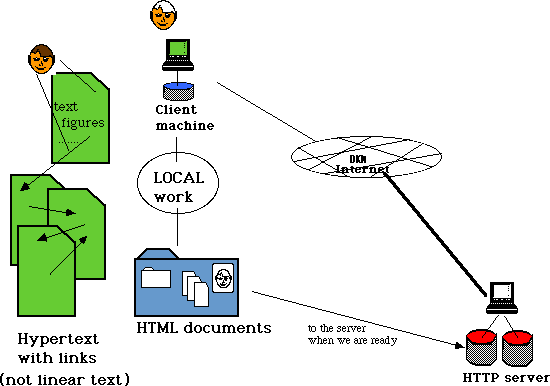
Figure 2
- We must try to think about the documents as being non-linear
(hypertext) and not a serially linked as in a book.
- Before we put our WWW-documents on the server we test the
functionallty and design in our own machine.
- Put your local HTML documents and directories on the server
using a FTP-client or by sharing directories on the local network.
|
|
|
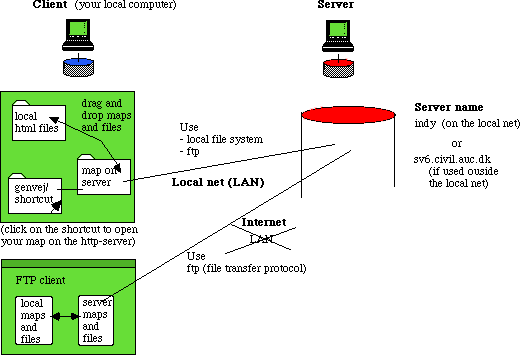
Figure 3
- When you are happy with the pages locally on your computer you
download the files to the server either using the local
area network, LAN, file sharing or a FTP-client.
- your personal homepage is reached at (the 'index.html' file in
your 'public-html' directory)
http://civil.auc.civil.auc.dk/~i6nn/
or more specifically at
sv6.civil.auc.dk/home/i6-3/i6nn/public_html
sv6.civil.auc.dk/home/i5-3/i5nn/public_html
sv6.civil.auc.dk/home/i5-1/i6nn/public_html
etc.
- You must mount the volume before you can reach your home page
area. (1) open top level directrory. (2) open directory HOME (3) change
directory to i6nn etc.
|
|
|
|
|








